Many people associate hair loss with men, but it's also a common concern for women.
Female pattern baldness, also known as androgenetic alopecia, affects millions of women around the world.
This article sheds light on this condition, exploring its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
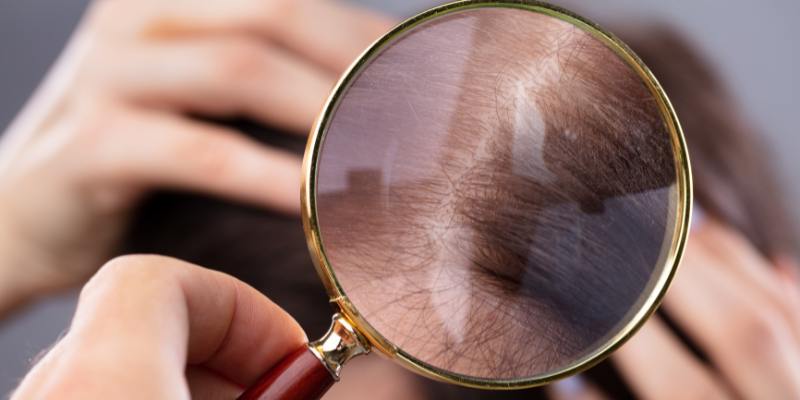

Understanding Female Pattern Baldness
Female pattern baldness is the most common cause of hair loss in women.
It can begin at any age but's more prevalent after menopause.
Unlike male pattern baldness, which typically presents with a receding hairline, female hair loss usually manifests as a gradual thinning across the scalp, often widening the part line.
Causes of Hair Loss in Women
Genetics plays a significant role in female pattern baldness.
Inherited genes can influence the sensitivity of hair follicles to hormones, particularly dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
DHT is a byproduct of testosterone and can shorten the hair growth phase, leading to thinner and finer hair over time. While hormonal changes are a key factor, other conditions can also contribute to hair loss in women.
These include:
- Telogen effluvium: This temporary hair loss is often triggered by stress, illness, childbirth, or significant weight loss.
- Thyroid problems: An underactive or overactive thyroid can disrupt the hair growth cycle and cause hair loss.
- Autoimmune diseases: Certain autoimmune diseases, like alopecia areata, can attack hair follicles and cause patchy hair loss.
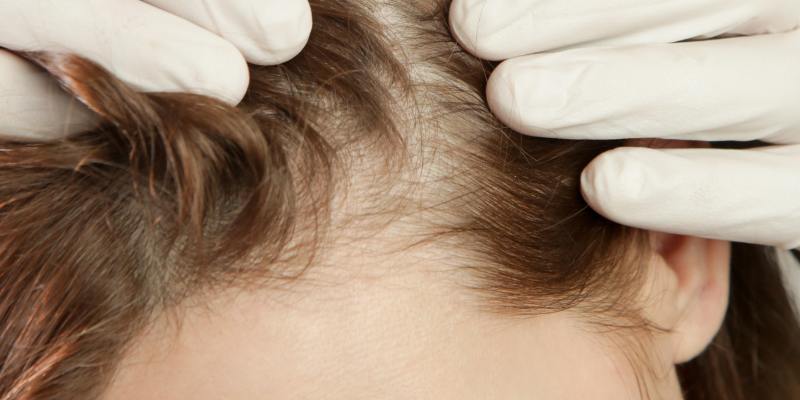
Treatment Options for Female Hair Loss
Fortunately, there are treatment options available to help manage female pattern baldness.
Here are some of the most common:
- Minoxidil: This topical medication helps stimulate hair growth and is available over the counter.
- Finasteride: This prescription medication can slow hair loss and promote some regrowth, but it's not recommended for pregnant or breastfeeding women.
- Cranial Prosthesis: Medical grade wigs are realistic and easy to wear. Most insurance companies cover the cost of a cranial prosthesis (medical wig).
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): This treatment uses low-energy lasers to improve scalp circulation and stimulate hair growth.
- Hair transplantation: In severe cases, hair transplantation surgery can be an option to restore hair density.
Taking Charge of Your Hair Health
If you're experiencing hair loss, it's important to consult a dermatologist or trichologist (a hair specialist) to determine the underlying cause and explore the best treatment options.
Early diagnosis and intervention can help manage hair loss and maintain a healthy head of hair. Remember, you're not alone!
Female pattern baldness is a common condition, and with various treatment options available, you can address hair loss and feel confident about your appearance.
Living with Hair Loss: Acceptance and Support
Hair loss can be emotionally challenging, impacting self-esteem and confidence.
Remember, you are not alone.
Many resources are available to support you, including online communities and support groups for women experiencing hair loss.
Embrace your personal style and explore different hairstyles that flatter your face shape and hair texture.
To add volume and fullness, consider wigs, hairpieces, or hair toppers. Our team comprises certified wig specialists who are expertly trained in cranial prosthetics. This ensures a perfect fit for your wig, creating a natural look that boosts your confidence.
We also carry a wide selection of high-quality wigs in various styles, materials, and colors. Finding the perfect wig that complements your personality and preferences is a breeze.

Top Five Things You Need to Know about Female Pattern Baldness
How common is female pattern baldness?
It is quite common and affects approximately one-third of susceptible women.
It can begin as early as puberty, but most women notice symptoms after menopause, when it is more likely to occur due to hormonal changes.
What are the symptoms of female pattern baldness?
The main symptom is a gradual thinning of hair, particularly at the crown and top of the scalp.
Unlike men, women rarely develop a receding front hairline.
How is female pattern baldness diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a medical assessment by a dermatologist who will examine the pattern of hair loss to determine if it's consistent with female pattern baldness.
Blood tests may be ordered to rule out other conditions that cause hair loss, and a scalp biopsy may sometimes be necessary.
What treatment options are available for female pattern baldness?
Treatment can vary depending on the severity of the hair loss and individual preferences:
- Minoxidil (Rogaine): The only FDA-approved medication for female pattern baldness, applied topically.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): For women in postmenopause, HRT can help manage hair loss by balancing hormone levels.
- Hair Transplants: Surgical options such as hair transplants are available but less commonly used in women than in men.
- Cosmetic options: Medical wigs and hairpieces can provide an aesthetic cover for hair loss and can be particularly effective as part of a comprehensive approach.
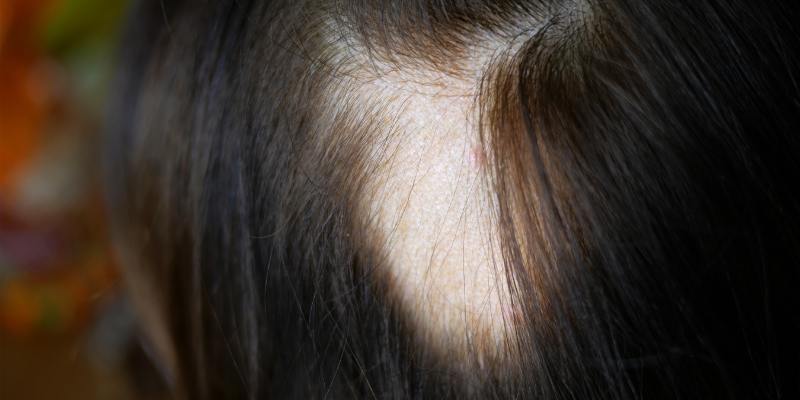
Can lifestyle changes help with female pattern baldness?
While lifestyle changes alone can’t reverse hair loss, they can help minimize its impact and support overall hair health:
- Nutrition: Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can support hair growth.
- Stress Management: Reducing stress through techniques like meditation, exercise, or therapy can help, as stress can exacerbate hair loss.
- Hair Care: Avoid harsh treatments such as hot rollers, curling irons, and chemical processes that can further damage thinning hair.
Don't settle for just covering up hair loss. Reclaim your confidence and embrace your beauty with Wig Medical.

